
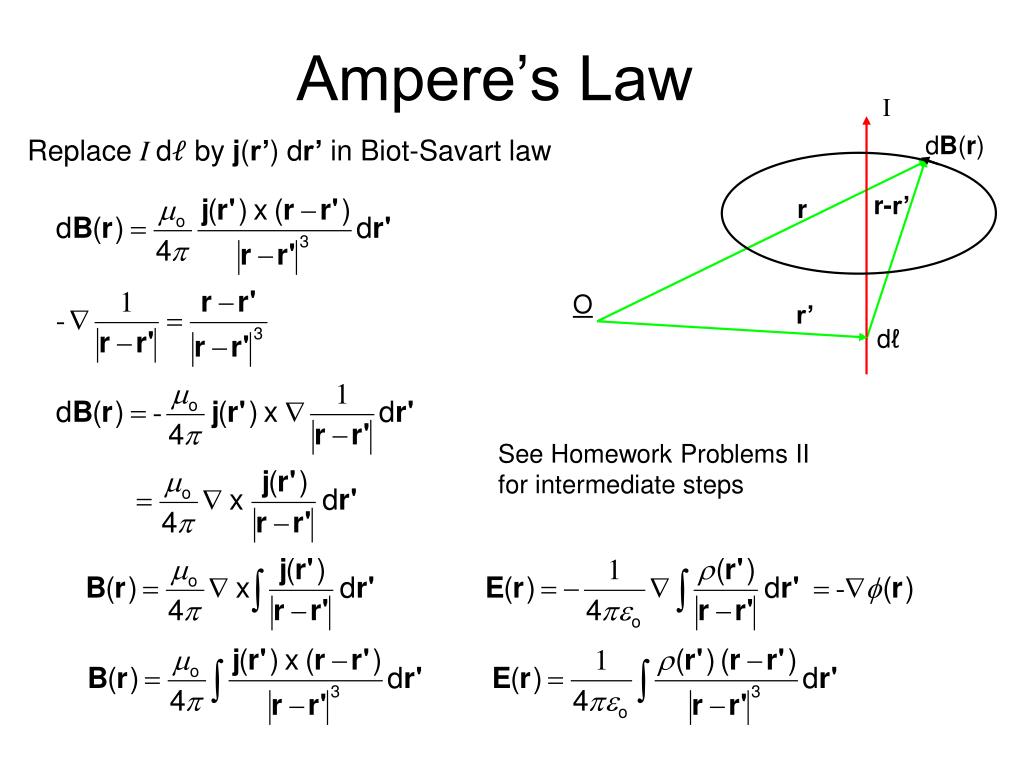
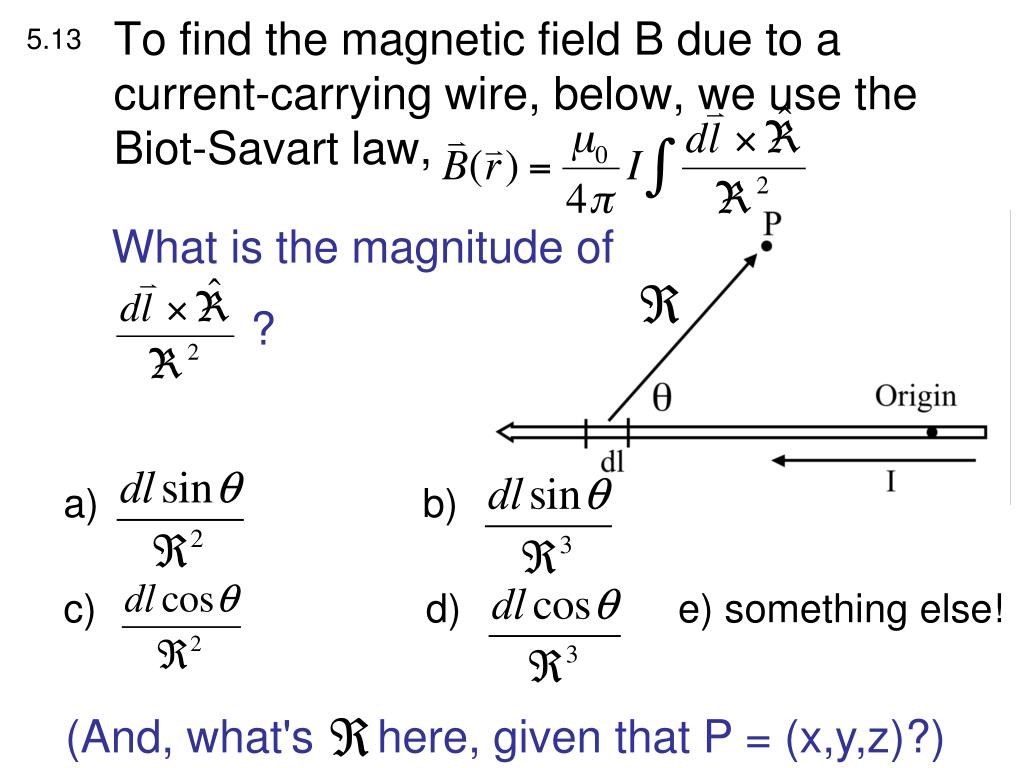
the distance of the electric current from the point within the magnetic field.The magnetic field produced by a current $I$ flowing through a wire can be determined by breaking the current path into short segments and adding all of the contributions of those segments together. The Biot-Savart law is a mathematical description of the magnetic field d that arises from a current I flowing along an infinitesimal path element d called the current element.
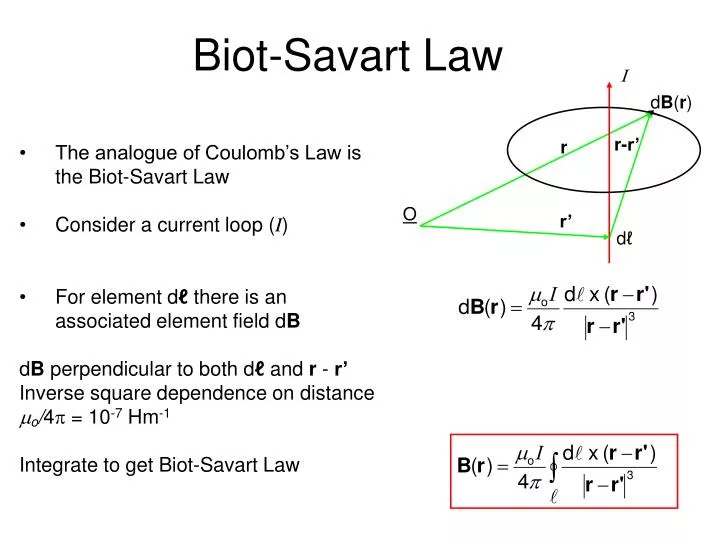
#Biot savart law free#
the length of the wire through which the current runs.Ĥ. The BiotSavart law originally was developed to find the magnetic field of a long wire, in order to explain the torque on a permanent magnet (a compass needle). The Biot-Savart law, also known as Ampres law or Laplaces law is equivalent to the steady state Maxwell equation in free space, and relates the a. The Biot-Savart law is used to calculate the magnetic field at a particular point, taking into account the following factors:Ģ. Biot Savart law states that the magnetic field due to a tiny current element at any point is proportional to the length of the current element, the current, the sine of the angle between the current direction and the line joining the current element and the point, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance of that point. While the electrical current moves in a straight line through a wire, the magnetic field is spinning around it. This law can be applied practically to calculate the magnetic field produced by an arbitrary current distribution. By integrating Laplace's equation over an infinitely long wire, the original integral form of Biot and Savart is obtained. Laplace gave a differential form of their result, which now often is also referred to as the Biot-Savart law, or sometimes as the Biot-Savart-Laplace law.
#Biot savart law how to#
Because a magnetic field is a spinning force (like the earth spinning around the sun, or the electron spinning around the nucleus in an atom), the Biot-Savart formula is useful not only in electromagnetics, but also in aerodynamics, for the analysis of vortexes.įrom other posts on electromagnetics ( Ampere’s Force Law) and experiments ( How to Make a Magnet), we know that an electrical current creates a magnetic field around the wire through which it flows. Biot and Savart interpreted their measurements by an integral relation. The Biot-Savart law is an electromagnetic formula that calculates the magnetic field created by an electric wire. It connects the magnetic field to the electric. In a similar manner, Coulombs law relates electric fields to the point. The Biot Savart Law is an equation that describes how a constant electric current generates a magnetic field. A current element is like a magnetic element in that it is the current multiplied by. The Biot-Savart Law relates magnetic fields to the currents which are their sources. Biot-Savart law magnetic field integration equations are derived for rod and plate elements, and for volume interface regions from an equation due to Wikswo. Biot-Savart law was created by two French physicists, Jean Baptiste Biot and Felix Savart derived the mathematical expression for magnetic flux density at a point due to a nearby current-carrying conductor, in 1820. The Biot-Savart law is named after two French scientists, Jean-Baptiste Biot and Felix Savart, who discovered it in 1820. A brute force method of finding the magnetic field due to a length of current-carrying wire. As mentioned earlier, the Biot-Savart law deals with a current element.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
